Premature ejaculation should be a cause for worry only if it occurs frequently. Someone may be diagnosed with the condition if he almost always ejaculates within one minute of penetration, can almost never delay ejaculation and feels distressed about the situation and tends to avoid sex as a result.
What Is Premature Ejaculation?
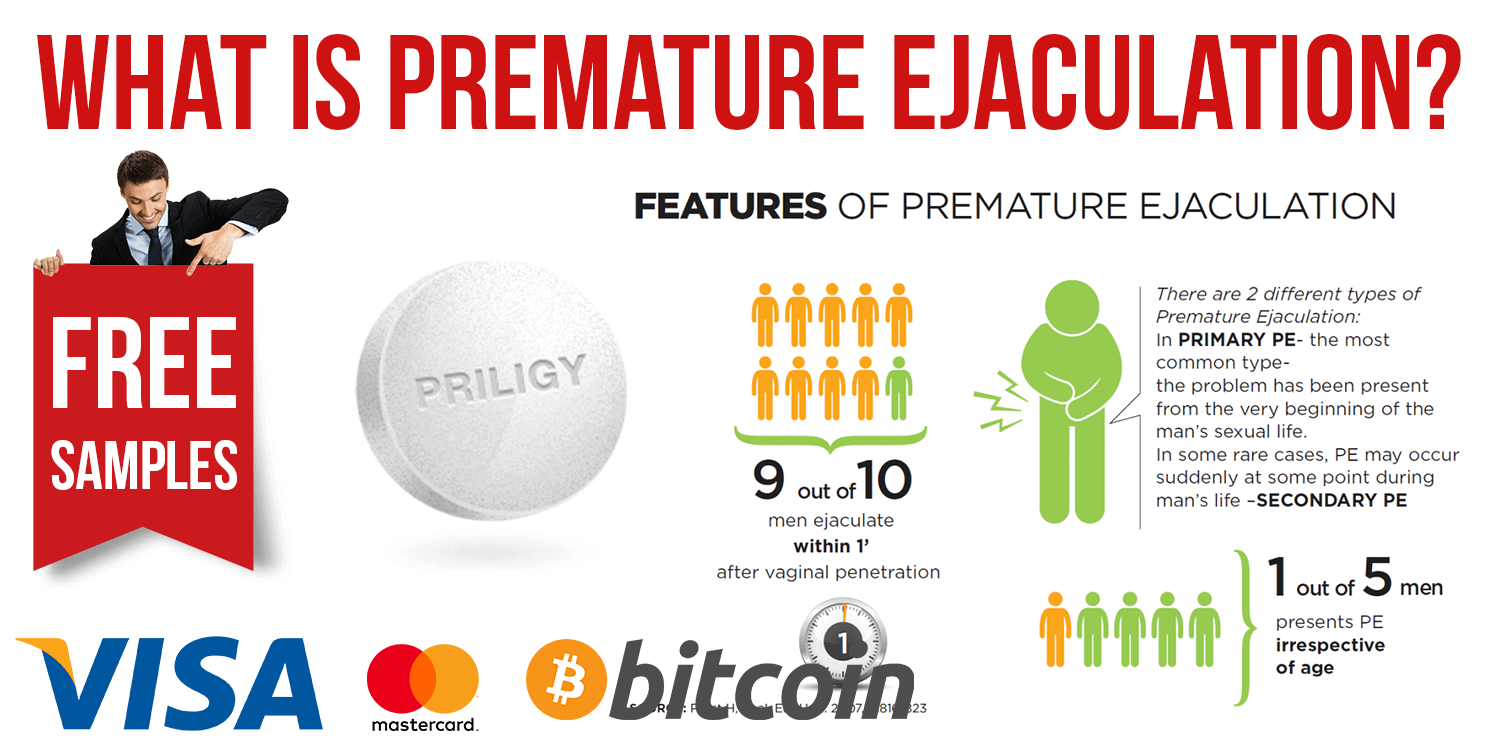
Premature ejaculation is one of the most common sexual concerns among men. One in three men say they have experienced it at one point in their lives.
Having occasional premature ejaculation symptoms are normal, but in cases where it becomes frequent or severe, it can become a more serious issue. In these cases, you should talk to your doctor.
What Is Premature Ejaculation?
The definition of premature ejaculation can vary. It can be defined as ejaculating sooner than one or one’s partner would like. A more serious diagnosis requires a more specific set of symptoms. The basic definition is an inability to control orgasm long enough to satisfy both partners.
Premature ejaculation should be a cause for worry only if it occurs frequently. Someone may be diagnosed with the condition if he almost always ejaculates within one minute of penetration, can almost never delay ejaculation and feels distressed about the situation and tends to avoid sex as a result.
What Causes PE?
PE is fairly common, but why does it happen? Both psychological and biological factors can play a role in causing premature ejaculation (PE).
The exact cause is not certain, but doctors do know that it results from a complicated interplay between physical and mental causes.
Some potential psychological factors include:
- early sexual experiences;
- depression;
- anxiety;
- poor self image;
- sexual abuse;
- relationship problems.
Worrying about PE can also worsen the condition, creating something of a vicious cycle. This worry may be especially pronounced in men with erectile dysfunction.
Some of the possible biological reasons for PE are:
- Abnormal hormone levels such as low testosterone.
- Atypical levels of neurotransmitter in the brain.
- Inflammation or infection of the urethra or prostate.
- Inherited traits.
Despite what some believe, having a small penis does not necessarily mean someone will also have PE.
Who Is at Risk for PE?
PE can happen to anyone, but certain factors make it more likely. The condition is thought to be inheritable, so if family members have PE, you are also more likely to have it.
Other health conditions including urethritis, prostatitis, hyperthyroidism, erectile dysfunction and obesity can all increase one’s risk of developing PE. Emotional and mental conditions, such as depression, anxiety, stress and relationship problems also increase risk.
Older men may be slightly more likely to develop PE.
What Are the Symptoms of PE?
The main symptom of premature ejaculation is not being able to stop oneself from orgasming within one minute of penetration. The problem can also occur without penetration, however.
If someone has had trouble with PE in all or almost all of their sexual encounters, including early ones, they may be diagnosed with lifelong, also known as primary, PE.
If the problem develops later in life after sexual experiences where PE was not an issue, you may be diagnosed with acquired, also known as secondary, PE.
If you have some symptoms of PE but not all, you may have natural variable premature ejaculation. This means that you experience periods of early ejaculation and periods where ejaculation time is normal.
Behavioral Techniques for Delaying PE
There is no universal solution to PE, but a combination of various methods may prove successful. What is good for every individual is different.
Certain behavioral techniques can be employed, which can help delay ejaculation. Masturbating an hour or two before sex is one such method.
Another is the pause-squeeze technique. This involves squeezing the part of the penis where the head meets the shaft for a few seconds when one feels like they are about to ejaculate. Once the feeling subsides, you can resume sexual activity. Repeat this as many times as necessary. Eventually, one may learn how stop ejaculation without this method.
The stop-start method works in a similar way. Whenever the man feels like he is about to orgasm, he and his partner should stop sexual activity until the feeling passes. This can also be repeated as many times as required.
Kegel exercises can also be used to help overcome premature ejaculation. These exercises strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which can be used to help control ejaculation.
Medications for PE
Certain drugs can be used for treating PE. Anesthetic creams and sprays numb the penis, because they contain numbing agents like benzocaine, lidocaine and prilocaine. They are applied to the penis 10 to 15 minutes before sex.
Some of these medicines are available over the counter and others are available by prescription. Some users have reported that sex is less pleasurable for both partners when using these drugs.
Condoms can also have a similar effect of reducing sensation. Some brands even make condoms specifically meant to reduce sensation.
Although not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), certain oral medications are sometimes used to delay ejaculation, such as antidepressants, analgesics and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors. These medicines could be taken daily or as need in order to treat PE.
Dapoxetine (or Priligy 60 mg) is believed to be the most effective antidepressant for treating PE. Others include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as sertraline (Zoloft), fluoxetine (Prozac), escitalopram (Lexapro) and the tricyclic antidepressant clomipramine (Anafranil).
Analgesics like Tramadol and Ultram are usually used to treat pain. Delayed ejaculation is one side effect. Tramadol can’t be used with SSRIs.
Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors are usually prescribed for erectile dysfunction but may also help people who suffer from PE. Examples of these PE medications include Tadalafil (Cialis), Vardenafil (Levitra), and Sildenafil (Viagra).
Delayed ejaculation is a side effect of these drugs. They also have some potential unwanted side effects.
| Medication | Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Antidepressants | Nausea, perspiration, sleepiness and lowered sex drive |
| Analgesics | Nausea, headache, sleepiness and dizziness |
| Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors | Headache, indigestion and facial flushing |
Counseling for Treating PE
Your doctor may suggest counseling to help with PE and its complications. Counseling may be most effective in combination with medication. How this is addressed may vary based on which doctor you see.
Counseling can help people with premature ejaculation do deal with stress, anxiety, depression of other mental health issues that may be contributing to or resulting from premature ejaculation.
Counseling related to relationship problems may also be of help. Relationship issues can both cause and be caused by PE. Relationship counseling or sex therapy can be an important step for curing premature ejaculation.
Other Methods for Treating PE
Other things to help premature ejaculation include diet, exercise and alternative medicine.
Condoms can also help PE by reducing sensation in the penis, similar to the way that anesthetic creams and sprays work. Some condoms brands even make condoms specifically designed to decrease sensation.
Some might suggest diets and offer tips on which foods prevent PE. Some believe that foods such as carrots, asparagus, eggs and dark chocolate can reduce symptoms of or even cure premature ejaculation.
In general, improving one’s diet and exercise can help with premature ejaculation, as it does with other health problems.
Some people also us alternative medicine to treat PE. Things like meditation, yoga, acupuncture and herbal remedies may help improve the condition, although their effectiveness has not been scientifically proven.
When Should You See a Doctor?
It can be uncomfortable to talk with your doctor about such a sensitive issue, but it is highly recommend that people who think they may have PE or symptoms of PE do so.
If you ejaculate sooner than you would like, you should talk to your doctor. If it is a frequent or especially severe issue, it is even more highly recommended.
Your doctor may suggest treatment or a talk with your doctor might provide comfort if they explain to you that occasional PE symptoms are normal. Either way, the talk will have been beneficial.
Premature ejaculation is the most common sexual dysfunction in the world. Many men have serious cases of the condition, and it affects almost everyone at least once in their lives.
Although it may be embarrassing to talk about or get help for, doing so can be extremely beneficial. Treating PE can improve your physical, mental, emotional and, of course, your sexual health.

 Free Viagra Samples 10 x 100mg
Free Viagra Samples 10 x 100mg Free Levitra Samples 10 x 20mg
Free Levitra Samples 10 x 20mg Free Cialis Samples 10 x 20mg Online
Free Cialis Samples 10 x 20mg Online