Male Urology Diseases and Problems
With great concern about our men’s health it is important to make an overview about the main urological diseases. It will help everyone to understand more about the conditions that every man may face in his life. When you are aware of something, you have the power to combat it.
What Are Urologic Diseases?
- What Are Urologic Diseases?
- Most Common Urologic Diseases in Men
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
- Urinary Incontinence
- Kidney and Ureteral Stones
- Prostatitis
- Bladder Cancer
- Enlarged Prostate
- Premature Ejaculation
- Infertility
- Peyronie’s Disease
- Urinary Tract Infections
- Kidney Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Other Urological Conditions
- How to Improve My Urological Health?
These diseases can affect women, men and children of any age period. In males, they usually involve the reproductive organs or the urinary tract.
Most Common Urologic Diseases in Men
The urinary tract performs the role of a draining mechanism to move away urine out of a body. Urine consists of water and wastes and the urinary tract includes kidneys, bladder and ureters.
To get rid of urine, the urinary tract system has to work altogether in a normal and correct way.
That is why all common men’s urology problems are the circumstances of urinary tract infections, kidney stones, prostate problems, bladder diseases, etc.
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a condition in which a man is not able to get or keep a hard and stable erection strong enough for satisfactory sexual intimacy. ED can be temporary or a long-term problem. A man can imply having ED in case:
- he gets an erection sometimes, but not every time when he wants to have sex;
- he gets an erection, but it doesn’t last long enough for satisfactory sex;
- he is not able to get an erection at all.

Sometimes men find it embarrassing and difficult to talk with a doctor about ED. Anyway, remember that healthful sex life conditions can improve your self-esteem and your life quality. Urologists are trained and accustomed to speak to people about many kinds of sexual problems. On the other hand, untreated disease can lead to depression, anxiety, inability to make a partner pregnant.
Many different factors can cause ED affecting your nervous system, vascular system and endocrine system.
Note that the following diseases can cause ED:
- high blood pressure;
- kidney disease;
- 2 type diabetes;
- heart and blood vessel disease;
- atherosclerosis;
- surgery for bladder cancer, radiation therapy or prostate surgery, if any.
This information will help your doctor understand your ED problem. The medical history can disclose diseases and therapy that lead to it. Reviewing your sexual activity can help to diagnose problems with sexual desire, ejaculation or erection.
A healthcare professional may ask you some personal questions that help to diagnose any psychological or emotional issues that may cause ED.
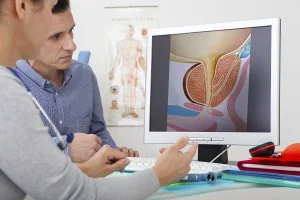
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
As we become older, our body undergoes alterations in ways that we are not always able to control. For many men, one of the problems that arises is that prostate becomes bigger. It’s a common part of aging process, but sometimes it can lead to a condition called Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia or BPH.
Prostate surrounds part of urethra, the tube that transfers semen and urine out of penis. When a man has BPH, his prostate is increased more than usual and it squeezes the urethra. In turn, it causes a weak stream when you urinate and makes you wake up often during the night to go to the toilet.
Talking about the reasons of this disease, doctors can not say for sure what is the exact cause. Some of them think it has something common with normal hormonal changes as men become older. At the age of puberty, men’s prostate doubles in its size. Later in life, at the age of 25, the prostate starts to enlarge again. For many men, this growth is happening for the rest of their life. But for some people it causes BPH.
When the prostate becomes bigger, it starts to compress the urethra. Men will experience certain unpleasant symptoms that affect urine stream and hurt. With the squeezed urethra, the bladder has to work more powerful to push urine out. When time passes, the muscles of the bladder become feeble, which makes it more difficult for it to empty. This can bring to the feeling as if you still have to pee even after you just visited the bathroom, or having to go too often – up to ten times a day, or incontinence.
A larger prostate doesn’t mean you should have more or worse symptoms. It’s peculiar for every person. Many men with very big prostates have none or few of these issues.
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is quite an embarrassing and more common problem as some people realize. It happens like an occasionally leaking urine (for example, on sneezing) or having an impulse to go to the toilet, which is so strong and sudden that you don’t get there in time. In other words, it’s an involuntary urine leakage, when a person has a weakened or lost control over the urinary sphincter.
More often, it occurs when people get older, but urinary incontinence is not an inevitable consequence of being old-aged. If this problem prevents you from daily activities, don’t hesitate to see a doctor. In the majority of cases, mere lifestyle changes or certain medical treatment can ease discomfort or stop urinary incontinence.
When the bladder and muscles involved in control of urine undergo sudden extra (physical) pressure, a man may urinate involuntarily.
The following conditions may bring to the incontinence:
- a sudden cough;
- heavy lifting;
- exercise;
- laughing.
Also, the following factors of risk are tied to men’s urinary incontinence:
- old age (the bladder and urethra muscles are weakening during old age);
- obesity (fat people experience enlarged pressure on their bladder and nearby muscles that make the muscles weak);
- smoking (men who smoke regularly are more likely to obtain a chronic cough, which can result in episodes of incontinence);
- prostate disease (male patients with a history of prostate surgery);
- some other conditions and diseases – men with diabetes, neurologic diseases, spinal cord injury, kidney or urine disease.
Kidney and Ureteral Stones
Kidney and ureteral stones can appear when a healthy balance of substances in urine, like minerals, salts and water is disordered.
Kidney stones are small-sized, usually from size of a grain of salt to a corn kernel. In many cases, men may feel nothing and never realize that they even have any until one of them goes on the move. Though many patients know about them, because flushing them out of the system as you go to the toilet can hurt.
The pain that a man feels is the main sign that his body has too much in the way of minerals and not enough in the way of liquid. This imbalance causes the formation of these rock-like objects. These stones may be of yellow or brown colour, either rough or smooth.
Symptoms may vary and can be different in severity, but one most common thing about them that is they can hurt. The patient feels the pain:
- in his abdomen or groin;
- in his back or side or below the ribs;
- when he goes to the bathroom;
- when he goes to the toilet more often than usually.
This pain can move to different body locations. It means that the stone is already moving from the kidney through the ureter and closer to the bladder. Sometimes, men can even see the stone come out, when they pee. A burning sensation may accompany urination process or blood may be found in the urine.
At the same time, stones may remain in the kidney for years without causing any problem. In addition to severe pain, such symptoms may occur like vomiting, general weakness, sweating, chills, fever, etc.
Several types of urinary stones can be differentiated:
- calcium stones (formed when there is too much calcium in the blood);
- uric acid stones (crystallized by excess uric acid);
- struvite stones (created by bacteria that infect the urinary);
- cystine stones (caused by large amount of certain amino acids).
Risk factors to develop urinary stones in men include:
- age (mostly they occur in men from 40 to 60 years old);
- diet and weight (occur in men on a diet high in animal protein or with overweight);
- lack of liquid (occur in men not drinking enough water);
- chronic urinary tract infections;
- increased alcohol intake;
- medical conditions (inflammatory bowel disease and gout can influence the normal balance of urine).
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is one of the most common urology problems. 10 percent of all males experience its symptoms. Men of any age can get prostatitis, but it is more spread among young and middle-aged people. This disease can be described as an inflammation of the prostate gland, which can be chronic condition or an acute illness. The inflammation can occur due to infection as well as because of other various causes.
The prostate gland is a detail of the men’s reproductive system, which is located at the forefront of the rectum and beneath the bladder. It circles the urethra, the tube through which semen and urine move away from the body. Its main purpose is to produce seminal liquid and to transfer sperm through the urethra. This seminal liquid protects and energizes sperm as it travels to a female egg.

- recent urinary tract infection;
- increased prostate gland;
- prior history of prostatitis;
- recent use of a urinary catheter or recent urologic procedure;
- engaging in rectal intercourse;
- local pelvic injury such as horseback riding or from bicycle riding.
The symptoms of prostatitis can vary depending on the cause of prostatitis. They may appear slowly or quickly, and can be cured rapidly or they can last for several months. The severity is usually most pronounced with acute bacterial prostatitis.
These are the signs that present in men with prostatitis:
- painful and/or frequent urination;
- sexual dysfunction or painful ejaculation;
- rectal pain, groin pain, abdominal pain;
- blood in urine;
- chills and fever;
- discomfort and body aches.
4 types of prostatitis with the symptoms can be differentiated:
| Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome | Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis | Acute (Sudden) Bacterial Prostatitis | Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis |
| Trouble and pain with ejaculation | Necessity to often urinate (mostly during the night) | Chills | No signs. It can be found while you’re being checked for other problems. |
| Trouble and pain with urination | Pain in the bladder, penis and testicles | Fever | |
| Pain in the bladder, penis and testicles | Feeling of burning in the process of urination | Severe burning while urinating | |
| Painful ejaculation | Trouble draining your bladder |
It is not quite clear, what is the cause of most cases of prostatitis. It can be initiated by bacteria that penetrate into the prostate gland from the urinary tract (the most common bacterial cause) and from direct extension or lymphatic spread from the rectum. It can also result from various sexually transmitted organisms. In many examples (especially in the chronic form of prostatitis) no specific cause of prostatitis can be found.
Bladder Cancer
In the majority of cases, bladder cancer has no indicative symptoms to be noticed and identified by, except hematuria (presence of blood in urine). However, often only one episode of hematuria is occurred and after that the urine appears to be transparent and clear. So, the patient forgets about it for long (even for the whole year) and, when the next case of hematuria takes place, cancer has been already claimed.
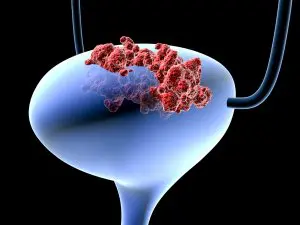
- pain in abdomen;
- painful urination;
- loss of body weight;
- weakness;
- loss of body weight;
- frequency in urination.
Such symptoms may also occur in many other diseases. So be attentive and alert once blood appears in the urine, it is compulsory that you have to visit an urologist without delay.
Enlarged Prostate
The men’s health condition with enlarged prostate is also called Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia or BPH. The information is provided in the same name clause.
Premature Ejaculation
Ejaculation is a process when semen is released out from a man’s body. Premature ejaculation (PE) is a condition, when ejaculation happens sooner than a man or his partner would like to happen during sex. Such PE is also called rapid or early ejaculation or premature climax.
Ejaculation is controlled by men’s central nervous system. When a man is sexually stimulated, the signals are sent to his brain and spinal cord. In case, he reaches a certain level of excitement, these signals are later on sent from his brain to the reproductive organs. Precisely this causes semen to be released through the penis.
PE is one of the most common sexual disorders in men from 20 to 60 years old. It can occur at any age.
Premature ejaculation can be described as:
- primary (when PE happens almost all the time at your first sexual encounters);
- secondary (PE occurs after when you’ve had previous sexual contacts without any problem).
Many males have natural variable PE, which includes periods of early ejaculation with the periods of a normal one. The cause of PE is not known enough. Medical studies show that premature ejaculation assumes a complex interaction of biological and psychological factors.

- worrying about premature ejaculation;
- early sexual experiences;
- poor body image;
- sexual abuse;
- depression.
Extra factors include:
- anxiety (many men have problems with anxiety about sexual performance or similar related issues);
- erectile dysfunction (men who are anxious to obtain and maintain an erection during sexual contact form a pattern of rushing to ejaculate, which is difficult to change);
- relationship problems (if a man has satisfying sexual relationships with other partners, where premature ejaculation does not occur, the reason is that personal issues between you and your partner are contributing to the problem).
Biological causes are illustrated by:
- inflammation and infection of the urethra or prostate;
- abnormal hormone levels;
- abnormal levels of brain chemicals called neurotransmitters.
Different factors can increase the risk of acquiring premature ejaculation:
- erectile dysfunction (if a man occasionally had a trouble in getting an erection, fear of losing the erection can force you to hurry through sexual encounters);
- stress (emotional and mental stress in any area of your life can limit men’s ability to relax during sexual intimacy).
Talk to your doctor if you ejaculate sooner than you wish. It is quite common and natural for men to feel embarrassed about discussing sexual problems, but don’t let it keep you from consulting a doctor. PE is a spread and treatable problem.
Infertility

The following sperm problems can be considered:
- low sperm concentration – the man ejaculates less semen compared to other men. Normal sperm concentration of a healthy man should be 20 million sperm per milliliter of semen. The count under 10 million denotes a low sperm concentration;
- low sperm mobility – sperm cannot “swim” as well as it has to;
- no sperm – when a man ejaculates there is lack of sperm in his semen;
- abnormal sperm – men’s sperm is of an unusual shape, what makes it more difficult to move and fertilize a woman’s egg.
Causes of abnormal semen can be of different nature:
- testicular infection, testicular surgery, testicular cancer;
- overheating the testicles (hot baths, frequent saunas, working condition in extremely hot environment condition can raise the temperature of the testicles. Even tight clothes may have the same impact on some people;
- ejaculation disorders – for some men it may be difficult to ejaculate properly. If ejaculatory ducts are blocked or obstructed a man can have a problem to ejaculate properly;
- undescended testicle – one (or both) testicle fails to descend from the abdomen into the scrotum during fetal development. Sperm production is influenced because the testicle is not in the scrotum. Healthy sperm requires to exist at a lower-than-body temperature. That is why they are located in the scrotum, and not inside the body);
- hypogonadism – testosterone deficiency can result in a disorder of the testicles;
- mumps – young children are usually affected by this viral infection.
However, if it occurs after puberty age, inflammation of the testicles may influence sperm production:
- radiotherapy and chemotherapy – such therapy can impact sperm production. The severity depends on how far from the testicles the radiation was targeted;
- some medications can decrease sperm mobility and count (Sulfasalazine – anti-inflammatory drug, anabolic steroids – taken by bodybuilders);
- illegal drugs and smoking – consumption of cocaine and similar substances.
Peyronie’s Disease

Many men suffering from this problem still can have sexual intimacy. But for some of them, it can be difficult or painful.
Therapists don’t know exactly why this disease appears. Many medical studies prove the plaque can form after some trauma that leads to bleeding inside the men’s organ and you may not even notice this injury.
Other cases, which develop over time, may be associated with genes. In some men, genes and injury can both be responsible.
This problem mostly occurs with men of middle age, and it becomes more common as a man becomes older. Symptoms may show up slowly or appear overnight. When the penis is soft, you can’t notice a problem. But in severe cases, the hardened plaque prevents flexibility and hurts so forcing the male organ to bend on erecting.
Sometimes minor forms of the problem disappear by themselves without causing pain or permanent bending.
Urinary Tract Infections

UTI symptoms will differ taking into account men’s age. In young men, UTIs are showed up by low abdominal pain in the process of urination, frequency of urination, burning sensation, and sometimes blood presence in urine. Elderly men suffer from such symptoms like fever, tremor, abdominal pain, fatigue. The urine can appear of dark colour or cloudy, sometimes with unpleasant smell. Usually UTIs do not cause fever, when the bladder is not infected. Fever can be a mark that infection has already affected kidneys (pyelonephritis) or prostate (acute prostatitis). These infections are dangerous for your life and require prompt hospitalization.
UTIs are the result of pathogenic bacteria or viruses that penetrate into the urinary tract and bring infection. According to medical researches, 12 percent of men have a UTI that causes noticeable symptoms. A burning sensation during urination is one of the symptoms of a UTI. Others include a frequent impulse to urinate and the feeling that the bladder is not fully empty. Antibiotics can usually combat most UTIs within five to seven days.
- bad urinary habits. It is a common practice to postpone urination when you are out and avoid going to the toilet, despite the fact how strong the urge for urination could be. Some men follow this practice for professional reasons (e.g. truck drivers). Such habits have to be cured, combining the prescribed medication with changes in everyday habits of urination;
- bad hygiene. It refers both to absence of daily hygiene of the genital zone and use of some sanitary products (e.g aroma baths that may cause irritation);
- urine stagnation. All urologists believe that wherever there is urine stagnation, there is an infection hiding. It increases the key role of regular voiding of the bladder. Any obstruction in the urinary tract inhibiting full urine release will sooner lead to UTI. Also, obstruction of kidneys or ureters causes Pyelonephritis. The stones cause microtraumas that become open gates for bacteria and stones themselves get infected. As a result, all therapies are out of result, because antibiotics cannot affect the stones;
- sexual practices. Sexual intimacy is the most frequent cause of UTIs. Following sexual contact, men get a great number of bacteria within their urine, which are normally discharged within 24 hours. So it is necessary to urinate after sexual intercourse. Another reason is applying of non-aromatic or aromatic lubricants that irritate and change our body defense.
- uro catheter. The catheter is used in male patients with inability to urinate. As it is an external foreign body to human organism, it brings a potential cause of infection.
- diabetes mellitus. UTIs are common in men with diabetes mellitus. When diabetes is not properly controlled, high sugar level in the urine becomes “food” for bacteria.
Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer (also called as renal cancer) is a disease in which kidney cells transform into malignant and start growing beyond control thus generating a tumor. Usually kidney cancer types first appear in the form of small tubes in the kidney. This kind of disease is called renal cell carcinoma. The good point is that in many cases kidney cancer is discovered before it is spread around a human body. In case, it is detected early it is easier to cure successfully. Sometimes this tumor can grow into a large one before it is revealed.
As you know, the kidneys are two organs in the shape of a bean. They are found in our lower abdomen on each side of your spine. Their primary function is to clean our blood, moving away wastes and making urine. Kidneys belong to urinary system, they also control the formation of red blood cells and regulate our blood pressure.
The following of kidney cancer types are known:
- urothelial cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis;
- squamous cell carcinoma;
- clear-cell sarcoma of the kidney;
- renal oncocytoma;
- reninoma;
- mesoblastic nephroma;
- angiomyolipoma.
Symptoms aren’t usually detected at the initial stages of kidney cancer. In the later stages, a patient may notice such symptoms like blood in his urine or a lump in the back, near the kidneys. Not so often he may feel a pain in kidney zone, fever, weight loss, anemia, fatigue and night sweats. So it is crucial to go to a physician if any of these symptoms take place.
Kidney cancer develops, when a change in the DNA of cell structure occurs. A genetic mutation forces cells to grow uncontrollably forming tumor cells. If not cured, it grows and spreads through the lymphatic system. Tumors grow as a single mass, but sometimes, more than one tumor can grow in one kidney, and sometimes in both kidneys.
Risk factors for renal cell carcinoma (the most common type of kidney cancer), include:
- age (the risk increases after 60 years old);
- obesity (people with extra weight have a higher risk because of hormones changes);
- sex (male is about two times as likely as female to obtain the disease);
- smoking (regular smokers have a twice higher risk);
- high blood pressure;
- having a family history of kidney cancer (the risk is higher in siblings);
- being black (the risk in black people is for no reasons higher than in whites).
If a man has these risk factors, it does not mean that he gets kidney cancer. And it’s also true that you can have none of them and still obtain the disease.
Prostate Cancer

- pain in urination;
- blood in semen;
- pain on ejaculation;
- frequent urination;
- difficulty or trouble on starting or stopping an urination.
The compression of the spinal cord is a true emergency sign and may be the first marker of cancer. It happens when the cancer has developed to the vertebrae of the spine and tailbone area. The weakened vertebrae can affect the spinal cord, causing its function problems.
At this stage the symptoms observed depend on the degree at which the spine is compressed. Ordinary symptoms that characterize acute spinal cord compression involve:
- enlarged difficulty on urination;
- tingling and numbness in the legs or groin;
- weakness in patient’s legs and difficulty in walking;
- problems in controlling your bladder.
These symptoms are often accompanied by a pain in the hip or back that can last up to a few days or weeks. Such health condition require immediate hospitalization in the nearest medical department. If not be treated immediately, it can result in permanent spinal cord damage.
Summarising this article, it is necessary to highlight that every man should undergo regular observation for prostate cancer. Every year men who are 50 years old and more should undergo a digital rectal examination and blood analysis for prostatic specific antigen (PSA).
Other Urological Conditions
Along with the already featured diseases some other common urological conditions can be diagnosed in men:
interstitial cystitis (also called painful bladder syndrome);
- overactive bladder;
- renal colic;
- renal cancer;
- nocturia;
- anuria/oliguria;
- orchialgia (testicular pain);
- penile and testicular cancer.
If you suffer from any of these symptoms, it suggests that you have problems in the urinary tract and have to consult an urologist:
- a frequent or urgent need to urinate;
- blood in your urine;
- pain or burning during urination;
- pain in your pelvis, lower back;
- urine leakage;
- trouble urinating.
A man should also consult an urologist if he experiences such symptoms:
- a lump in the testicle;
- a decreased sexual desire;
- troubles to get or keep an erection.
How to Improve My Urological Health?
The primary care provider can treat a man with minor urinary problems, such as a UTI. And he may delegate a patient to an urologist, if the symptoms don’t improve and disappear or if a man has conditions that need other kind of treatment. In some cases, a man even needs to consult a specialist for certain conditions – an oncologist, a cancer specialist.
Follow the below mentioned instructions to stay healthy far away from the urologist consulting room:
- limit the consumption of caffeine and salt;
- stay within a healthy weight limit;
- quit smoking;
- drink cranberry juice to prevent urinary tract infections;
- limit fluid intake during nighttime hours.
Talk to your therapist and try some medication especially developed to help men to combat certain sexual problems. Erectile dysfunction treatement by Viagra or Kamagra pills with their active ingredient sildenafil. Sildenafil has an ability to block the action of an enzyme known as PDE5, a substance that causes smooth muscles to relax. Due to widening of blood vessels the muscle vasodilation and relaxation is reached.
As an alternative to the above mentioned pills try Super P Force and Tadapox. You can choose the right variant depending on the dosage and desired effect you want to achieve.
Dapoxetine (or Priligy) will help you to cope with premature ejaculation. It is not a pill that will actually cure PE, but it can be used as supplement to the treatment prescribed by your doctor.
All drugs are always available online with round the clock service at ViaBestBuy. Every man will or sure appreciate this impersonal way of purchase with quick delivery option.
So, it is important to remember that every other man is the best advocate for his own urological health. Schedule regular checkups with your therapist and always report any concerning symptoms you develop.

 Free Viagra Samples 10 x 100mg
Free Viagra Samples 10 x 100mg Free Levitra Samples 10 x 20mg
Free Levitra Samples 10 x 20mg Free Cialis Samples 10 x 20mg Online
Free Cialis Samples 10 x 20mg Online


 interstitial cystitis (also called painful bladder syndrome);
interstitial cystitis (also called painful bladder syndrome);